Cloud CDN Technologies – Not as far as it Looks

So, you have launched a website, hosted your server with the best provider but your customers are still complaining about poor site performance. They say the website loads too slow; a fraction of your visitors even abandoned your website before it could display a character. Research showed that a delay of just 1 second can cause a 7% loss of visitors which could lead to loss of web traffic on your website.
Hopefully, you now realize the seriousness of the issue we are addressing here. A second might seem insignificant, but it is not. Also, if you continue to be even a bit complacent about your website’s performance, you are getting nowhere.
Disclaimer: The blog throws light on an ever-evolving concept called CDN, which can scale your site’s speed, embellish SEO metrics, and increase time on site. Exit at your own risk.
Here is very short story about our blog. When we first started blogging, we opted for the cheapest host we could then find. We had not the slightest idea that performance is the frontline of customer acquisition. To knock more sense into the last statement – “Customers Buy Products that Convey Value”. So, a visitor can hang on for longer on your website if: –
- There is no other place one could find content available on your site
- Performance adds to your site’s value
So we started writing stories, poems and eventually started to have visitors on our WordPress blog. The impressions we received were actually increasing day after day for months until the day it went down, and it sudden fell drastically. It happen because we uploaded too much content than WordPress blog could handle. The loading speed was tremendously low. In some cases, we heard people complaining that they had waited almost a minute for articles to load.
Content Delivery Network
It is all normal at this moment for you to contemplate where the problem started in the first place.
Just think we were running a website (and the server) from Texas. A quarter of website traffic comes from London, another from Sydney (Australia), and the remaining from Delhi (India) and New York.
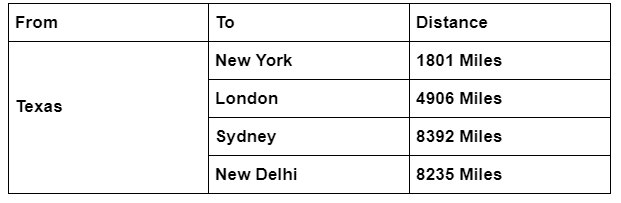
Geographically, We were closest to New York, with the distance being around 1800 miles and farthest from Sydney, with the two cities separated by a distance of almost 4900 miles.
Every time somebody opens up our WordPress blog, a series of requests is made to the server. At the same time the requests are granted files is transferred to the end-user. This transmission takes place through undersea cables back and forth.
Because we have been an amateur blogger, and poor as well, have servers at only one place, but visitors from all around the world. So, the same server that is catering to requests from New York is also sending articles to New Delhi.
This transmission (requesting permission and receiving files) takes place in a matter of milliseconds and is directly proportional to the distance between the two points.
Below, we have arbitrarily assumed some data for our understanding –

Thus, a user based in New York might not face as many problems but user in Sydney or New Delhi face many issues. During rush hours, our WordPress blog saw a huge surge in web traffic and unfortunately crashed almost every alternate day.
Relocating server was not a solution either. Even if we had relocated it, where would we have it moved? Doing so would have solved the problem in one city and creating issue in the other city.
For most of the time, the site was either out of service or running so slow a turtle would outrun it, frankly speaking. Our WordPress blog’s performance took a dig in terms of the number of visitors. Within a couple of months our WordPress blog visitors shrunk to 10 per day of which not less than 8 visits were my own. We need a solution to this problem. So after further research, we get to know about CDN (Content Delivery Network).
CDN (Content Delivery Network) solves this problem. It brings the content closer to the end-user, thereby reducing the distance between the content and the user.
What may have caused such stress on the network?
It takes content 40 milliseconds to reach New York and 187 seconds (almost 4.5 times) to reach Sydney. The duration of a blink itself is around 400 milliseconds. So, 40 or 180 msec, what difference does it make when contents in both cities are rendered within the blink of an eye? Again, the problem is not the distance but the server. My server was so minimalist in terms of performance it could not cater to more than 200 visitors at one time.
This combined with the long distances where files were supposed to be delivered, culminated us in shutting down my blog forever. Not only CDN solutions very unpopular during those days, but also, we would not have spent a penny extra on our blog; especially when the hosting provider had already emptied my piggy bank.
When some users went off my site and the load came within the deliverable limits of the server, the website loaded so smoothly as if it never crashed.
What Content Delivery Network could do?
We are now sure that you have now understand what Content Delivery Network could do. It is a grid of servers, apart from your root server, that distributes and then caches files to cater to requests thenceforth.
Say, we had cached our content with a delivery network with CDN points in New Delhi, Melbourne, and Manchester. Now, where do you think the requests are likely to be catered from? From the CDN point nearest to the user, obviously.
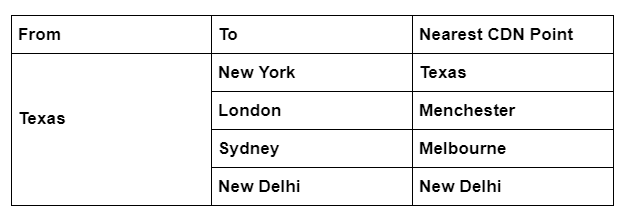
CDN points may be distributed all throughout the world. A single country may have multiple hot points or none at all. For our blog, if our CDN service provider allowed us to choose hot points, We would have placed them all in India and a few near London – most of our WordPress blog traffic came from these two regions.
Now, if a request is made for an article in Toronto, where do you think this request can be best catered to?
The best CDN practices to cache content
Even though the files are now fetched through CDN points, the base server is still the root of everything and anything on your website. Even the best CDN won’t work until files are cached to the distribution network. Content caching to CDN servers is unlike copying files from one storage drive to the other. Two CDN techniques are currently in use: –
- The Push CDN – had we rejuvenated our WordPress with push CDN, We would be forcing files from my root server (at Texas) to the delivery network, which would then send it to all its notes. Thus, Push CDN achieves caching by the uploading of static data on the root server.
- The Pull CDN – the pull CDN will not have those files that are not requested by the users even once. When a request is made, it first goes to the nearest CDN point, where the system checks whether the files are yet available in its servers. If no, CDN point redirects the request to the root server, delivers the content to the user, and finally distributes them throughout its network.
There is nothing particularly good or bad in CDNs types. The PULL network is ideal for cases where there is a tremendous amount of data in the server and not all of it is used with the same frequency. This technique is the most useful for websites with a number of pages, many of which sit idle and barely have visitors.
PUSH is rather more open in terms of compatibility and supports a range of requirements. Though, it can be somewhat more expensive than its cousin PULL.
Can CDN technologies lead to conversion?
Business conversions are dependent upon two factors –
- Number of leads
- Relevancy of lead
Obviously, the more leads you have in your bucket more the customers you can approach for business. This is also evident from the fact that Stores have a large amount of crowd in them generate the maximum sales.
As long as you are targeting correct keywords, the relevancy of leads is not something you should worry about. Websites that have complained of irrelevant leads in the past had either wrong backlinks or targeted incorrect keywords on some pages.
Page load speed and performance are two important characteristics search engines have increasingly drawn their focus to. Because CDN enhances the page load characteristics, your site will experience a significant SEO boost.
Further, when we had the idea of using CDN for myself, we were skeptical because our content would go to a foreign server. With over time it was made aware that CDN uses caching algorithms and canonical headers to enhance SEO. This mean that Google would not have punished our blog for duplicating content – the canonical makes sure both CDN and original server can serve one source, through different locations.
Takeaway – Where could you Deploy CDN solutions?
CDN is useful for websites that get traffic from several locations around the world. Additionally, the traffic should be healthy enough to invest in CDN. It might not pay off investing in CDN to cater to traffic during spike hours only. If your server can handle visitors pretty well, then there is a sudden surge, you should consider scaling the server instead. When the situation is such that a large number of visitors maneuver on your site simultaneously, there is no escaping CDN.





