Secure Your Cloud Server With Zero Trust Policy

Contents of Table
Today, where cloud servers in India have become the backbone of modern businesses, security is paramount. As we navigate this dynamic terrain, a question looms large: How can we fortify our cloud servers against an evolving array of cyber threats? The answer lies in a revolutionary approach – the Zero Trust Policy.
According to Gartner’s report, by 2026, approximately 10% of large enterprises are anticipated to implement a well-developed and quantifiable Zero-Trust program. This statistic makes us rethink our approach to cloud server protection.
What is Zero-Trust Security?
The traditional approach to cybersecurity involved designating certain zones as secure, operating under the assumption that threats originate exclusively from outside the network’s perimeter. This flawed perspective, however, became evident as evolving cyber threats exposed the risks associated with placing trust solely in location-based connections.
The Zero Trust security model revolutionizes this conventional concept by advocating for the assumption that threats could exist on any channel. According to this framework, the key to maintaining security lies in the continuous verification of all elements. By adopting this approach, organizations introduce additional obstacles for hackers attempting to breach protected company data.
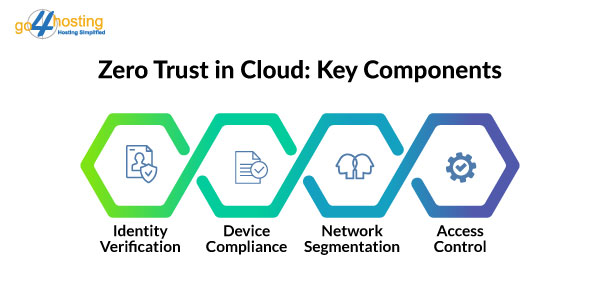
Key components of the Zero Trust model in cloud hosting in India include:
1. Continuous identity verification
2. Device compliance enforcement
3. Network segmentation
4. Application-access based control
5. Least privileged access for users
Implementing these requirements not only aligns the organization with the principles of the Zero Trust model but also establishes a robust defense against potential security breaches.
Why Zero-Trust Security in Cloud Server is Gaining Popularity?
As reported by IDG, over 73% of companies currently deploy applications or infrastructure in cloud hosting in India. These cloud environments, managed by cloud service providers and SaaS vendors, exist independently of an organization’s network, leading to a departure from conventional network control measures.
Consequently, many companies face challenges such as:
Applications and data are dispersed across various locations.
Limited visibility into user access and device usage due to assets residing on third-party infrastructure.
Uncertainty surrounds the utilization and sharing practices of data.
To tackle these issues, organizations employ diverse access technologies based on asset location, resulting in a fragmented security architecture. Cloud servers in India diverge fundamentally from traditional networks, undergoing constant evolution. It necessitates that a company’s security strategy be both all-encompassing and flexible. This unified security architecture should offer the following:
1. Secure user access to applications and data across public cloud, SaaS applications, and private cloud/data centers.
2. Controls and limits access to assets while defining usage parameters.
3. Regularly inspects traffic and enforces ongoing security policies.
The Zero Trust fulfills the requirements mentioned above in a cloud server in India.
Steps for Implementing Zero Trust in the Cloud
Embarking on the journey of implementing Zero Trust for cloud security requires careful planning and strategic steps. Each Zero Trust security implementation is unique, reflecting specific company goals and addressing distinct challenges. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process effectively:
Step 1: Define Your Objectives
Before diving into implementation, clarify the objectives of adopting Zero Trust. Establish specific company goals that Zero Trust will help address. This clarity ensures that the desired outcomes and their value align with your organization’s unique requirements.
Step 2: Catalog Your IT Assets
Create a comprehensive catalog of all your company’s IT assets. It includes identifying sensitive data storage, third-party applications in use, various assets, and critical services. Understanding the scope of your company’s IT landscape is essential for devising an effective protection plan.
Step 3: Map Out the Infrastructure
Connect the dots by mapping out the interactions among different IT components. Analyze how sensitive data is collected and transmitted to reveal insights into your business operations. This process helps identify critical areas that require heightened attention and security measures.
Step 4: Develop a Template for Cloud Orchestration
Create a framework detailing how your existing infrastructure can be orchestrated through cloud hosting in India. Establish clear boundaries between teams, users, and their applications. Ensure there are no overlaps that could compromise data security. This template serves as a guide for maintaining a secure and well-organized cloud environment.
Step 5: User Access Management Plan
Formulate a user access management plan that clearly outlines permissions for specific content. Implement the principle of least privilege access, allowing users access only to materials necessary for their work functions. This approach enhances control over data flow and strengthens security when accessing the cloud servers in India.
Step 6: Continuous Maintenance and Monitoring
Regularly inspect your setup for misconfigurations and inefficiencies. Incorporate ongoing maintenance and monitoring as integral components of your implementation plan. Active monitoring not only identifies potential issues but also expands the protection surface, serving as an additional security countermeasure.
Wrapping Up

The journey toward securing cloud servers in India has reached a crucial juncture, and the Zero Trust Policy emerges as the beacon guiding us through the evolving landscape of cyber threats. It reshapes our approach by instilling a foundational belief—trust nothing, verify everything.
A unified security architecture, as advocated by Zero Trust, becomes imperative. It provides a secure way for users to access resources, manages the accessibility of assets, and ensures continuous enforcement of security policies. It spans across public cloud, SaaS applications, and private cloud/data centers.
Take the first step toward a more resilient and secure digital future with go4hosting. For comprehensive security solutions aligned with the principles of Zero Trust, reach out to our team today!
FAQs
- How does Zero Trust work in the cloud?
Zero Trust in the cloud operates on the foundational principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within certain network perimeters, Zero Trust challenges this notion by requiring continuous verification of all entities trying to access resources. In cloud hosting in India, this translates to rigorous identity verification, device compliance checks, network segmentation, application-based access controls, and enforcing the principle of least privilege. By adopting Zero Trust, organizations enhance their security posture, mitigating the risks associated with dispersed data, diverse access points, and the dynamic nature of cloud environments.
- What is the zero trust limit?
The term “zero trust limit” refers to the foundational concept of Zero Trust security. It operates on the premise that trust cannot be automatically granted to any entity, whether within or outside the network. Within a zero-trust model, trust is never presumed, and verification is mandatory for every user, device, and application seeking access to resources. This approach emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls, minimizing the potential attack surface and enhancing overall security in dynamic digital environments.
- Is Zero Trust in the cloud easy to implement?
Implementing Zero Trust in the cloud servers in India can vary in complexity depending on the organization’s existing infrastructure and processes. While the concept may seem straightforward, the actual implementation involves strategic planning, a thorough understanding of IT assets, and a commitment to continuous monitoring. It’s crucial to define clear objectives, catalog IT assets, and create a template for orchestration. While it may pose challenges, the enhanced security and adaptability provided by Zero Trust make it a valuable investment in the long run.





